When I first started managing servers at VMHoster, one of the most common questions I’d get from clients was: “What’s the difference between SSD and NVMe, and which one should I choose?” Honestly, I had the same confusion years ago when these terms started floating around.
Here’s the thing – the terminology can be misleading. Many people think SSD and NVMe are competing technologies, but they’re not exactly apples-to-apples. Let me break this down in a way that actually makes sense.
Understanding the Basics: What Are SSDs and NVMe?
Before we dive into comparisons, let’s clear up some confusion about what these terms actually mean.
SSD (Solid State Drive) refers to any storage device that uses flash memory instead of spinning disks. Think of it as an umbrella term. Unlike traditional hard drives with moving parts, SSDs store data on interconnected flash memory chips, making them significantly faster and more reliable.
NVMe (Non-Volatile Memory Express), on the other hand, is a protocol – basically a set of rules for how your computer communicates with storage devices. It’s specifically designed to take advantage of the speed of modern flash storage by connecting directly through PCIe lanes.
So when someone says “SSD vs NVMe,” what they usually mean is “SATA SSD vs NVMe SSD.” Both use solid-state technology, but they connect to your system differently.
The Real Difference: It’s All About the Connection
The main distinction comes down to how these drives talk to your motherboard.
Traditional SSDs typically use the SATA interface (the same connection old hard drives used). While this was a massive upgrade from HDDs, SATA has a bottleneck – it maxes out around 600 MB/s. That might sound fast, but in 2025, it’s actually limiting.
NVMe drives connect via PCIe (Peripheral Component Interconnect Express), which is like giving your storage a direct highway to your CPU instead of making it take side streets. A PCIe 3.0 NVMe drive can hit speeds of 3,500 MB/s, and newer PCIe 4.0 drives? We’re talking 7,000 MB/s or more.
When you’re running virtual machines or hosting multiple websites on a VPS hosting plan, those speed differences become incredibly noticeable.
Performance Showdown: Numbers That Matter
Let me share some real-world numbers I’ve observed while managing server infrastructure:
Sequential Read/Write Speeds:
- SATA SSD: 500-550 MB/s read, 450-520 MB/s write
- NVMe SSD (PCIe 3.0): 2,000-3,500 MB/s read, 1,500-3,000 MB/s write
- NVMe SSD (PCIe 4.0): 5,000-7,000 MB/s read, 4,000-6,000 MB/s write
IOPS (Input/Output Operations Per Second): This is where NVMe really shines. SATA SSDs typically deliver around 90,000-100,000 IOPS, while NVMe drives can push 500,000+ IOPS. If you’re running databases or applications with lots of small file operations, this difference is game-changing.
When Does NVMe Actually Matter?
Here’s my honest take: not everyone needs NVMe. I know that sounds counterintuitive, but let me explain.
You’ll benefit from NVMe if you’re:
- Running virtual machines with multiple operating systems
- Hosting high-traffic websites with lots of concurrent users
- Working with large databases that require frequent read/write operations
- Editing video or working with large media files
- Running game servers where load times matter
- Managing dedicated server environments with demanding applications
SATA SSD is perfectly fine if you’re:
- Running a small personal blog or portfolio site
- Hosting a few low-traffic websites
- Using basic shared hosting needs
- On a tighter budget
- Building a simple file storage server
For most small businesses and personal projects, a quality SATA SSD will serve you well. The jump from HDD to any SSD is massive; the jump from SATA SSD to NVMe is noticeable but not always necessary.
Price Considerations: Is NVMe Worth the Premium?
The good news? NVMe prices have dropped significantly over the past few years. Back in 2019, you’d pay almost double for NVMe compared to SATA. Today, the gap has narrowed considerably.
As of 2025, you might pay only 20-30% more for an NVMe drive with similar capacity. For hosting providers, this premium often translates to just a few dollars more per month on your hosting plan – a worthwhile investment if you need the performance.
At VMHoster, we’ve seen more clients opting for NVMe storage on their cloud hosting plans because the cost difference has become minimal while the performance boost remains substantial.
Form Factor and Compatibility
SATA SSDs typically come in the standard 2.5-inch form factor – the same size as laptop hard drives. They’re universally compatible with any system that has a SATA port.
NVMe drives usually come in the M.2 form factor, which looks like a small stick of gum that plugs directly into your motherboard. They’re compact and elegant, but you need a compatible M.2 slot that supports NVMe (not all M.2 slots do – some only support SATA).
For server environments, this matters less since modern server motherboards come equipped with multiple NVMe-capable slots. But it’s something to consider if you’re upgrading older hardware.
Reliability and Lifespan
Both SATA and NVMe SSDs use similar flash memory technology, so their lifespan is comparable. The measure you’ll want to look at is TBW (Terabytes Written) – the total amount of data that can be written to the drive over its lifetime.
A typical consumer-grade SSD (whether SATA or NVMe) might have a TBW rating of 150-600 TB, while enterprise drives can handle several petabytes. For most hosting scenarios, either option will outlast its usefulness before it wears out.
One advantage of NVMe is better thermal management in newer models, though high-performance NVMe drives can generate more heat and may require heatsinks in intensive applications.
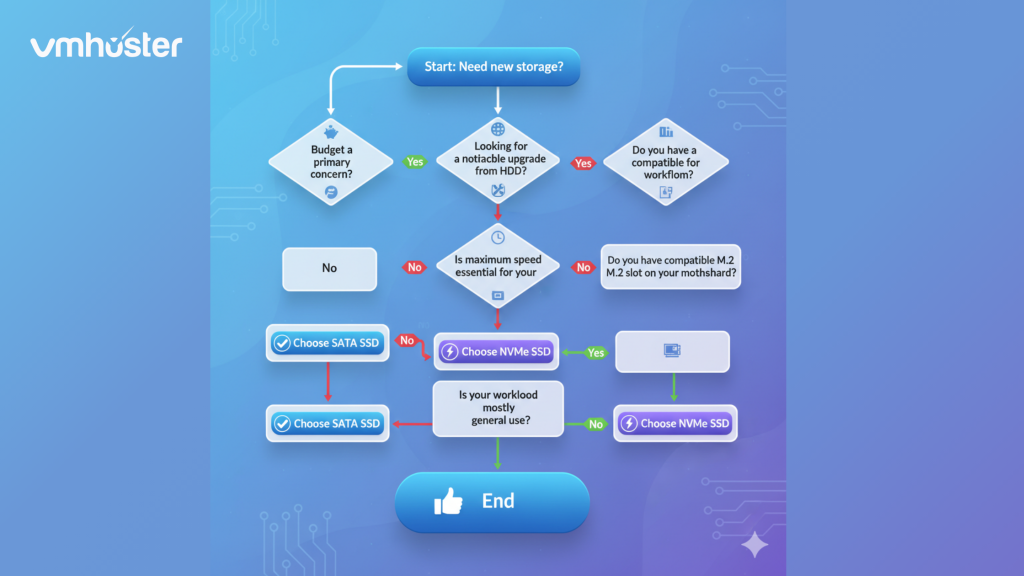
Making Your Choice: What I Recommend
After managing hundreds of server deployments, here’s my practical advice:
Choose SATA SSD if:
- Budget is your primary concern
- You’re running simple web hosting or file storage
- Your current infrastructure doesn’t support NVMe
- You’re upgrading from traditional HDDs (you’ll already see massive improvements)
Choose NVMe if:
- You need maximum performance for demanding applications
- You’re hosting databases or running virtual machines
- The small price premium fits your budget
- You’re building a new server from scratch (future-proofing)
For most of our VMHoster clients, I recommend NVMe for VPS and dedicated server plans, especially when running resource-intensive applications. The performance improvement justifies the marginal cost increase, and it helps ensure your infrastructure won’t become a bottleneck as your needs grow.
The Bottom Line
The “SSD vs NVMe” debate isn’t really about one being better than the other – it’s about understanding that NVMe is the newer, faster interface for SSD technology. Both are solid-state drives; NVMe just has a faster connection to your system.
If you’re currently running on traditional hard drives, upgrading to any SSD will transform your experience. The jump from HDD to SATA SSD is enormous. The jump from SATA SSD to NVMe is noticeable, especially for demanding workloads.
For hosting needs, consider your specific use case, budget, and growth plans. Sometimes SATA SSD is perfectly adequate; other times, NVMe’s performance is exactly what you need to keep your applications running smoothly.
Need help deciding which storage solution is right for your hosting environment? Our team at VMHoster can help you assess your needs and recommend the perfect configuration for your VPS hosting requirements.
Additional Resources:
- Understanding Server Storage Technologies – TechPowerUp
- NVMe Specifications – NVM Express Official Site
- SSD Endurance Explained – AnandTech Storage Reviews